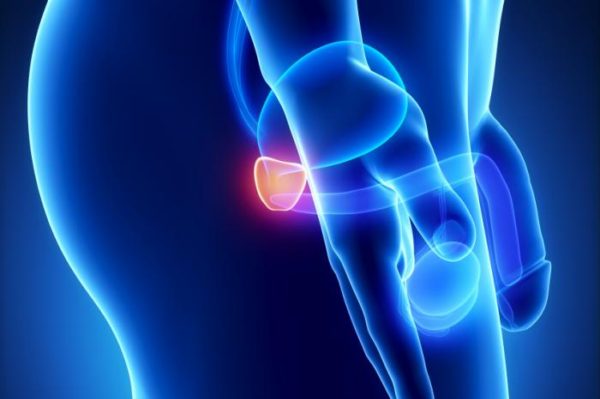
The prostate gland is a small gland below the bladder. It is divided into two lobes, to the left and right of the urethra (the tube that carries urine from the bladder to the penis). The main function of the prostate is to produce the fluid that combines semen with sperm cells from the testicles.
PSA is the protein made by the prostate gland. Some of the protein leaks into the blood. A higher PSA level is an indication of an issue. There are some factors that cause some men to have higher levels than others: age, ethnicity, medical procedures, some medications, an enlarged prostate or a prostate infection.
The American Cancer Association reports that 1 in 7 men will be diagnosed with prostate cancer in their lifetime. Prostate cancer is the 2nd leading cause of cancer deaths in American men (lung cancer is the first).
Prostate exams reduce the morbidity of the disease collaboration software. The ACA’s recommendations for screening are as follows:
40 years of age — Men with one or more 1st degree relative who had prostate cancer at an early age.
45 years of age — Men who are considered high risk: African Americans and men who have a father, brother or son diagnosed younger than 65 years of age.
50 years of age — Men at an average risk of cancer and expected to live a decade or more.
The two main tests used to screen for prostate cancer are the digital rectal exam (DRE) and the prostate specific antigen test (PSA). Neither test confirms prostate cancer, but it can detect signs of a problem. Further testing and/or a biopsy may be necessary.
Digital Rectal Exam (DRE)
The DRE is a preliminary screening for prostate cancer. If you have hemorrhoids or anal fissures, please inform your doctor or nurse prior to your exam, as it may cause discomfort. The doctor or nurse will glove and lubricate his or her finger and insert it into the rectum. He or she will palpate the back of the gland to feel for any abnormalities (Prostate cancer usually begins at the back of the prostate gland). If no further testing is necessary, you will be able to return to your daily activities.
Prostate Specific Antigen Test (PSA)
The PSA is a blood test that measures the protein levels made by the prostate. The PSA is highly advised for men who fall within the recommended age range for testing. To ensure an accurate result, refrain from ejaculating for 48 hours or exercising heavily for 48 hours. If you have a urinary infection or have had a prostate biopsy within the last six weeks, please wait until you are healed. Excessive activity, ejaculation and infection can raise PSA levels and deliver a false positive. Results from the blood test may take up to 14 days.
Read the full article here.
Comments are closed.